函數 (Function)
令, 為兩個 metric spaces
函數的定義
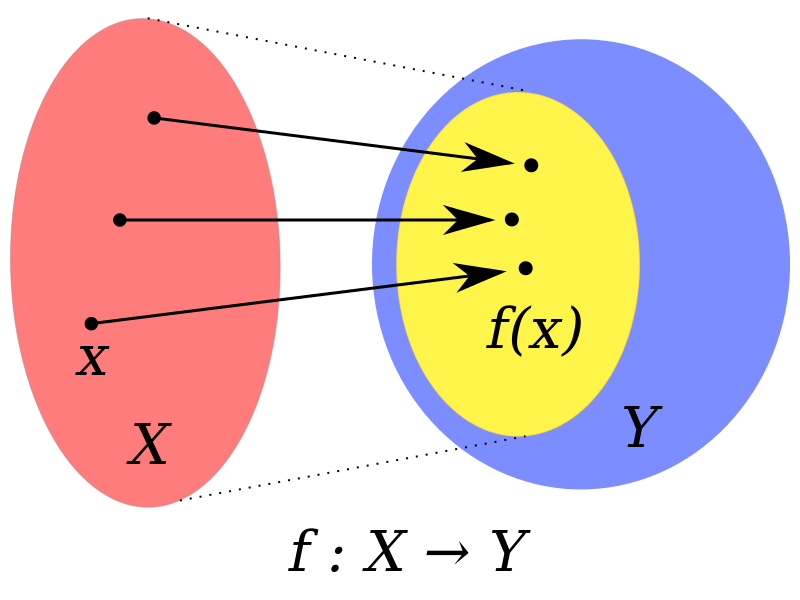
is a function if .
為 的定義域(domain),記為.
為的值域(range),.
依上述定義,可為一對一或是多對一函數,但不可為一對多函數。
- (one-to-one, bijection) and then .
- (onto, surjection) .
- , 而onto為 ,此時函數可能為one-to-one或many-to-one.
- and but 不符合函數定義。
一對多的情形在代數中稱為映射(mapping)或是關係(relation)。
函數必須是one-to-one時,inverse relation 才是函數。因one-to-one時才可避免invese時one-to-many的情形發生。
若集合與集合間存在1-1的函數時,稱兩集合有相同的基數(cardinal number),即兩集合的元素個數相同;或稱兩集合等價(equivalent),此時該1-1函數為等價關係(equivalence relation),即滿足reflexive, symmetric, transitive。
E.g. 自然數與整數為等價集合。
- E.g. ,與為等價集合。
- E.g. 與實數為等價集合。
Image and pre-image
If , , the is the image of .
If , , is the pre-image (inverse image) of
E.g. .
- The image .
E.g. , and .
- 若令, 則.
- Theorem: Every infinite subuset of a countable set is countable.
由定理可知,一個可數的集合之子集合必為可數集合,而不可為不可數集合。
連續函數 (Continous function)
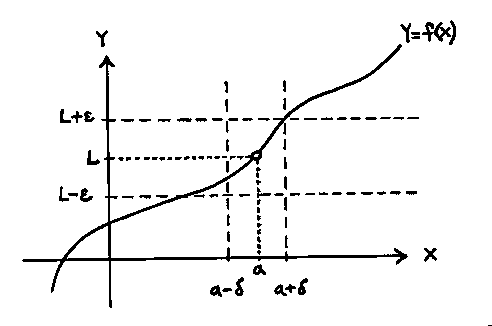
is a function, is continuous at a point if
- .
如果在集合中每一點都連續時,稱 is continous on 。
下圖為的範例。
函數的最小上界與最大下界性質
- Theorem:雙變數連續函數的最小上界的交換性
- 函數 有上界。
- 則.
- Theorem:雙變數函數最小上界與最大下界的不等式
- 函數之值域為有界集合。
- 則.
函數的極限 (Limit of functions)
- Let , and a function .
is a limit point of , and it is written if
- .
注意,,但不一定在集合中。(如不在有理數集合中)。
For every sequence such that and , then .
If has two limit points at and , then . (極限點唯一存在)
- Theorem: is continuous function if is open set for every open set .
Proof:
"" Suppose is open in and is continuous.
and
.
is open.
"" and, is open and contains , so it conains some ball about , this means is continuous at .