機器學習介紹 (Machine learning introduction)
: feature domain (input), range (output)
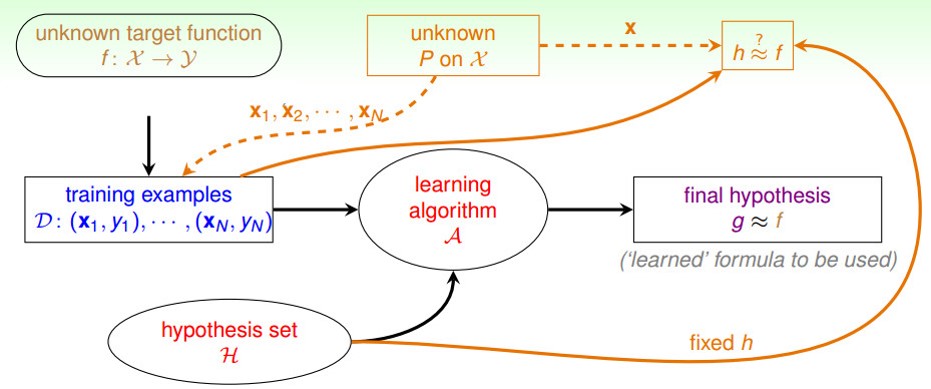
, 將資料由feature轉換到classification (如果為regression)的函數,其解析形式未知,只有部份資料集合被觀測到。
假設資料集合的特徵的定態(stationary)機率分佈為。
訓練資料的由未知的資料分佈隨機抽取樣本而產生,然後及其目標值被提供給學習器,學習器在學習目標函數時的定義域為假設集合 (set of function)。
在觀察了一系列訓練資料後,學習器需要從假設集合中得到最終的假設(函數),這是對資料集合未知分佈的目標函數的理想估計函數。
最後,我們通過訓練出來的假設對中新的資料的性能來評估訓練器(leave-one-out, K-fold cross-validation or other unobserved samples)。
Example: 核定信用卡問題
- 以下為某個使用者的個人信用資料,請問是否應核準其信用卡的申請?
| 欄位 | 值 |
|---|---|
| age | 23 |
| gender | female |
| annual salary | NTD 1,000,000 |
| year in residence | 1 year |
| year in job | 3 year |
| current debt | 200,000 |
- 因此input .
- output :核準, :拒絕。
- unknown target function .
- hypothesis: .
- 目標是使機器學習模型的函數 逼近未知的真正目標函數 .
Machine learning and data mining
- ML: use data to compute hypothesis that approximates target f.
DM: use (huge) data to find property that is interesting.
If "interesting property" == "hypothesis that approximate target"
- then ML == DM
Machine learning and artificial intelligence
AI: compute something that shows intelligent behavior.
g approximates f is something that shows intelligent behavior
- ML can realize AI, among other routes.
- eg. chess playing.
Machine learning and statistics
statistics: use data to make inference about an unknown process.
g is an inference outcome;
- f is something unknown
- statistics can be used to achieve ML
- traditional statistics also fcous on provable results with math assumptions, and care less about computation.